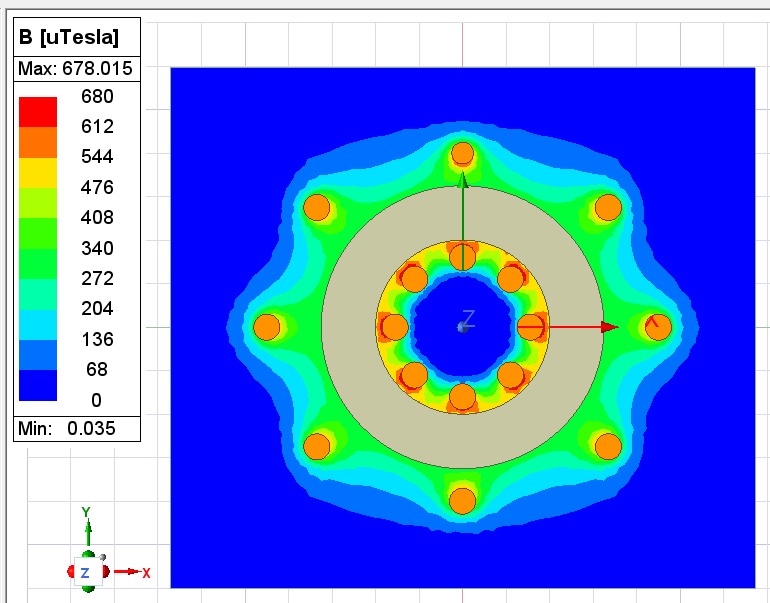
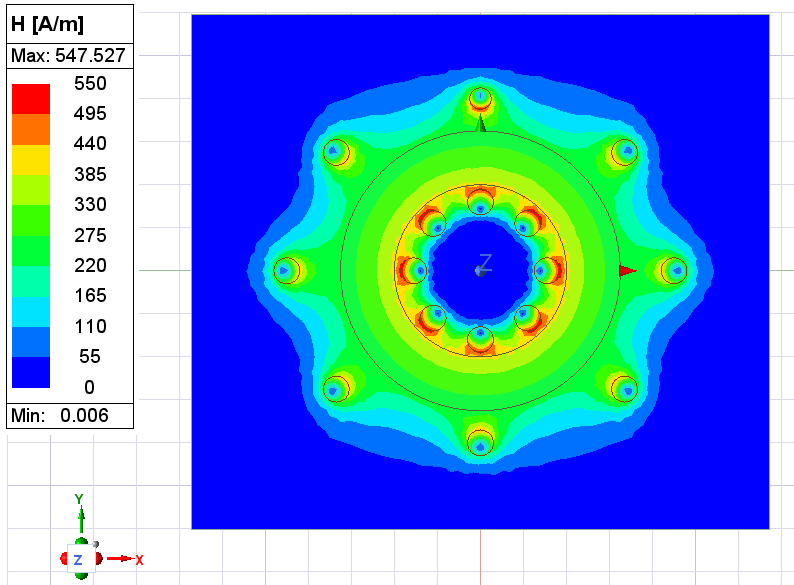
Project Description: 2D Magnetic Field Simulation for an 8-Coil Toroid Inductor
CAD Modeling of the Toroidal Coil System
The project began with the creation of a 2D CAD model of an 8-coil toroid. Each coil was accurately represented with precise spacing and curvature around a central toroidal core. The modeling process ensured geometric fidelity to support realistic electromagnetic behavior and compatibility with mesh refinement during simulation. Attention was given to the curvature continuity of coil windings and core alignment to support uniform magnetic coupling.
Electromagnetic Simulation Using Ansys Maxwell
The CAD model was imported into Ansys Maxwell (2D), a finite element solver specifically designed for electromagnetic field simulation. Material properties, such as copper conductivity for the coils and nonlinear magnetic permeability for the toroidal core, were assigned. A transient magnetic analysis was performed to evaluate flux distribution, magnetic field strength, and symmetry. Current excitations were applied to each coil to observe interactions between magnetic loops, and results confirmed flux linkage with minimal leakage, validating the toroidal configuration. The simulation also ensured that the design avoided magnetic saturation and maintained low core losses under operating conditions.
Thermal Analysis and CFD Coupling in Ansys Fluent
To assess thermal performance, Joule heating results from the electromagnetic simulation were exported and used as input for thermal analysis in Ansys Fluent. Heat generated from current-carrying conductors was analyzed under natural and forced convection scenarios. CFD simulations were run on the 3D CAD model to study airflow behavior around the toroid, identifying hot spots and evaluating the efficiency of passive cooling. This coupled simulation approach ensured that both magnetic and thermal limits were respected, contributing to safe operational conditions.
Conclusion and Application Insights
The multi-physics simulation approach provided a deep understanding of both the electromagnetic and thermal performance of the toroidal coil system. Field plots, vector visualizations, and thermal maps demonstrated effective coil symmetry, robust magnetic flux containment, and manageable heat dissipation. The outcomes support practical applications in areas such as power electronics, magnetic confinement systems, wireless charging infrastructure, and transformer design, where controlled magnetic behavior and efficient thermal management are essential.
Project Takeaways
This project emphasized the importance of a multidisciplinary simulation approach to achieve a well-rounded and functional electromagnetic system. By combining CAD modeling, electromagnetic simulation in Ansys Maxwell, and thermal-fluid analysis in Ansys Fluent, the project ensured comprehensive system validation. Key takeaways include the necessity of early design accuracy for mesh quality, the impact of material selection on both electromagnetic efficiency and thermal safety, and the benefits of simulation-driven design in optimizing system performance prior to prototyping. These insights will guide future work in designing high-performance, thermally reliable, and electromagnetically efficient toroidal systems for demanding engineering applications. Due to proprietary confidentiality rules, only selected parts of the field plots and data were retained for presentation.